Samanid Dynasty Facts For Kids
The Samanid dynasty was a powerful Persianate Sunni Muslim empire that played a vital role in the revival of Persian culture and science.

Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
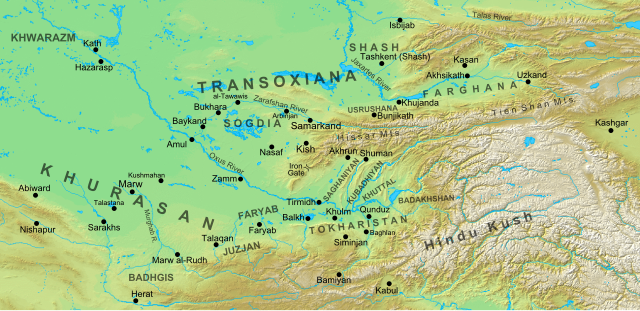
The Samanid Dynasty was an important empire in Central Asia that existed from 875 to 999 AD. 🌟It was mainly located in areas that are now modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and parts of Afghanistan. The Samanids were known for their love of culture, learning, and art. 🎨This time was very exciting because the Samanids helped spread the Persian language and literature. They were also known for being very good at governing and encouraging trade between different regions! 🌍
Gallery of Samanid Dynasty Facts For Kids
Notable Rulers
One of the most well-known rulers of the Samanid Dynasty was Ismail Samani. He was a strong leader who ruled from 874 to 907 AD. 🏆Under his leadership, the dynasty expanded and became powerful. Another important ruler was Nuh I, who governed from 943 to 954 AD. He also promoted culture and the arts! 🎭The Samanid rulers were smart and made friends with other leaders to keep peace in their lands, which helped the empire grow even more.
Decline And Legacy
The Samanid Empire began to decline in the late 10th century due to invasions from other groups, like the Ghaznavids and Seljuks. ⚔️ Despite losing control, their legacy lived on! The Samanid achievements in culture, trade, and learning laid the groundwork for future Persian empires. 🎓Many of their literary works and artistic styles continued to be appreciated and built upon in later centuries. They are still celebrated today for their impact on the region’s history! 🌟
Art And Architecture
Samanid art and architecture were truly stunning! 🏛️ They built beautiful mosques and palaces with intricate designs. The Samanid mausoleum in Bukhara is a fantastic example of their architecture, known for its brickwork and dome! 🌙The artwork included colorful tiles, calligraphy, and decorative motifs that reflected the rich culture of the time. This architectural style influenced many future generations in the region! 🎉
Economic Innovations
The Samanid Dynasty was famous for its trade and economy! 💰They developed trading routes connecting China, India, and Europe, making cities like Bukhara and Samarkand essential hubs for commerce. Merchants traded silk, spices, and precious metals. 🛍️ The Samanids also introduced new coins that made buying and selling easier. Their strong economy helped their empire flourish and supported art, learning, and culture!
Religious Influences
The Samanid Dynasty was a Sunni Muslim empire. ☪️ This means they practiced a branch of Islam. They built many mosques, where people could pray and learn about Islam. The Samanids were known for being tolerant of different religions, allowing Christians, Jews, and Zoroastrians to live peacefully in their empire. 😊This created a unique blend of cultures and ideas that strengthened their society!
Cultural Achievements
The Samanid Dynasty is famous for its many cultural achievements! 🎉The rulers supported poets, writers, and artists. One famous poet from this time is Ferdowsi, who wrote the “Shahnameh,” a great book that tells stories of Persian kings and heroes! 📚The Samanids also built beautiful gardens, mosques, and schools. Their love for learning created a golden age for Persian culture, making cities like Bukhara and Samarkand famous throughout the world! 🌸🕌
Territorial Expansion
The Samanid Empire grew bigger and bigger! 📈It expanded over a large area, covering parts of modern Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and Iran. This empire reached its height during the 10th century when it controlled important trade routes, connecting Europe and Asia. 🛤️ The Samanids allowed people of many religions to live in peace, which helped their empire become a bustling center for trade and culture! 🌞Merchants and travelers rushed to their cities to buy, sell, and share ideas.
Literature And Science
During the Samanid Dynasty, literature and science thrived! 📖🔥 The empire encouraged writers and scholars, many of whom wrote important books. Great poets like Ferdowsi and Omar Khayyam wrote timeless masterpieces! Moreover, scientists like Avicenna made significant discoveries in medicine and philosophy. 🧪🔬 Schools and libraries were established, fostering a love for knowledge that inspired generations to come!
Origins Of The Samanid Dynasty
The Samanid Dynasty began with a man named Saman Khuda, who was a dehqan landowner in the early 800s. 🌾His descendants became powerful leaders in the region. The dynasty grew strong under Ismail Samani, who ruled from 874 to 907 AD. He unified several small territories and built a strong state! 🏰The Samanids were Persian-speaking and promoted Persian culture, creating a bridge between different cultures and peoples in Central Asia.
Relations With Neighboring States
The Samanid Dynasty had many relations with neighboring states! 🌍They traded and interacted with the Byzantine Empire, India, and China. The Samanids often made alliances through marriages and diplomacy to keep peace. 🤝However, they also faced conflicts and invasions from rival empires like the Turks and the Ghaznavids. Despite these challenges, the Samanids maintained a remarkable level of cultural exchange, enriching their own empire and the world around them! 🌈
Samanid Dynasty Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required