Electric Charge Facts For Kids
Electric charge is a basic property of matter responsible for electric interactions, existing in two forms: positive and negative.
Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
Electric charge is a tiny thing we can't see but is very important! ⚡It makes things work like your toys, computers, and even lightning! Everything around us has electric charge—like people. There are two types: positive and negative. You can think of positive charge like a sunny day ☀️ and negative charge like dark clouds 🌧️. When they stick together, they help things work, but when they don't, things can get zappy and spark! Electric charge is part of science and helps us understand how many things around us work!
Gallery of Electric Charge Facts For Kids
Coulomb's Law
Coulomb's Law is a special rule created by Charles-Augustin de Coulomb in the 18th century. It tells us how strong the electric force is between two charges. 🤝The closer the charges are, the stronger the push or pull! For example, if you have a balloon with a negative charge and a positive charge from your hair, they will attract each other! 🌪️ This law helps scientists figure out how electric charges work all the time, in batteries, motors, and even during lightning strikes! ⚡
Types Of Electric Charge
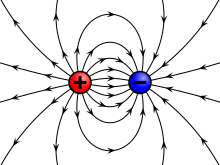
There are two main types of electric charge: positive and negative. 🔆Positive charges come from protons, found in the middle of atoms (the building blocks of everything!). Negative charges come from electrons, which buzz around outside the atoms. When you rub a balloon on your hair, it gets a negative charge! This is because it takes electrons from your hair. 🦸♂️ When a positive charge meets a negative charge, they attract each other like best friends. But when two positive or two negative charges get close, they push each other away!
Conductors And Insulators
Materials can be conductors or insulators depending on how they handle electric charges. Conductors like metals (copper, aluminum) allow the electric charge to flow easily! ⚙️ That’s why wires are often made of copper. On the other hand, insulators like rubber and glass don't let the electric charge move through them easily. 🏠This is important because it keeps us safe from electric shocks while using tools and gadgets! Choosing the right materials helps keep our homes and cities powered safely! 🛡️
Electric Charge In Nature
Electric charge is not only in gadgets and machines; it's also everywhere in nature! 🌍Thunderstorms create lightning, a big spark of electric charge that can light up the sky! 🌩️ Also, little creatures called electric eels, found in South America, can produce a strong electric charge to zap prey or protect themselves! 🐍Also, some plants and animals use electric charge to communicate, like the electric fish! This shows that electric charge is a big part of our world, from weather to wild animals! ⚡
Electric Fields And Forces
An electric field is an area around a charged object where other charged objects feel a force. 🌐Imagine blowing up a balloon until it feels full—when you let go, it zooms away! That's similar to how electric fields work. They stretch out in all directions! If you bring a positively charged balloon near a negatively charged piece of plastic, the electric field creates a force that pulls them together! ⚡This helps us understand how electricity flows, making our lights, phones, and other gadgets work! 💡
History Of Electric Charge
The idea of electric charge has been around for a long time. In 600 B.C., a Greek philosopher named Thales discovered that rubbing amber (a type of fossilized tree resin) with animal fur created a spark! ⚡Later, in the 1700s, scientists like Benjamin Franklin studied it more. Franklin named electric charges "positive" and "negative." How cool is that? 🎩By the 1800s, more discoveries were made, like the battery by Alessandro Volta in Italy! Batteries help store electric charges, making them important for modern technology! 🔋
Applications Of Electric Charge
Electric charges are super helpful and used in many ways! 🛠️ Batteries keep our toys and electronic devices running, while electrical circuits power our homes. 🚦Without electric charge, we wouldn’t have electricity for lights, computers, or even video games! Electric charges also help us send messages through the air—think of your favorite cartoons streaming online! 📺Scientists are even studying how electric charge can be used in new technologies like solar panels for clean energy! 🌞
Future Directions In Electric Charge Research
Scientists are always learning new things about electric charges! 🔬They are exploring ways to make batteries last longer, use less electricity, and help reduce pollution. 🚗Some are even working on ways to use electric charge in super-fast cars! Scientists hope to create "quantum computers" that use super small electric charges to perform many tasks at once! 🌌This will help solve big problems quickly. By studying electric charges, they aim to make our world safer and more fun! ⚡
Electric Charge Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required