Dawn Facts For Kids
Dawn is the magical time that marks the beginning of twilight before the sun rises, illuminating the sky in beautiful colors.

Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
Dawn is the magical time when night turns into day. 🌅It happens just before the sun rises, painting the sky with beautiful colors. Scientists call this time "twilight." At dawn, you can see shades of pink, orange, and purple as the sun starts to peek above the horizon. This beautiful show happens every day, but the times can change based on where you are and the season! For instance, in New York City, dawn can happen as early as 5:00 AM in summer and around 7:30 AM in winter. Isn’t nature awesome? 🌎
Gallery of Dawn Facts For Kids
Dawn Phenomena
Dawn brings fascinating phenomena that can surprise us! 🌈One of these is called the “green flash,” a quick burst of green light seen just before sunrise. People also witness beautiful halos and rainbows when conditions are right. Sometimes fog or mist makes dawn look dreamy! The clouds can create spectacular shapes as the sun rises. Every dawn is a little different, and that’s what makes it so special! Look out for these surprises next time you greet the day! 🎉
The Science Of Dawn
Dawn happens because of Earth's rotation! 🌍Earth spins on its axis, and as it turns, different places get light from the sun. When the sun is just below the horizon, it creates that soft, glowing light we see. The atmosphere bends sunlight, making the sky look brighter. Scientists call this bending of light "refraction." During dawn, birds wake up, and flowers start to open, as everything comes alive! It’s like a secret signal that a new day is beginning! 🌼
Dawn Around The World
Dawn is celebrated differently in various parts of the world! 🌏In Sydney, Australia, people often visit the beach to enjoy the sunrise. In Egypt, visitors to the Pyramids watch the sun rise over the ancient stones, creating magical shadows. In India, many gardens bloom at dawn, attracting bees and butterflies! Each place has its own unique way of celebrating dawn, using its beauty to connect people with nature and culture. 💖
Different Types Of Dawn
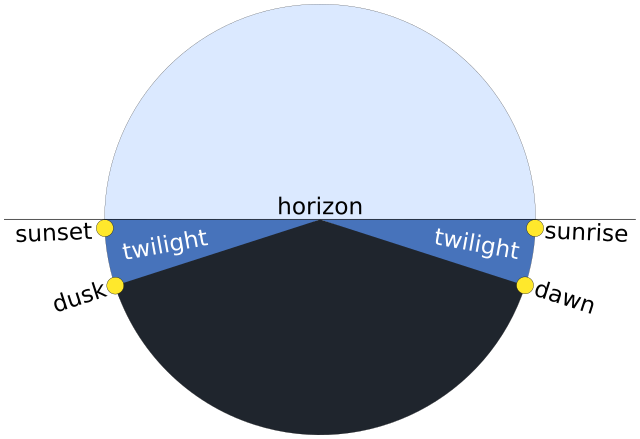
There are three different kinds of dawn: Civil, Nautical, and Astronomical. 🌅Civil dawn is when it's bright enough for people to see without lights. Nautical dawn is when sailors can start to see the horizon, while Astronomical dawn is when the stars start to disappear from the sky. Isn’t that cool? 🌌The type of dawn can sometimes change depending on where you are in the world. For example, in places close to the North and South Poles, the types of dawn can last longer.
Dawn And Human Activities
Humans also enjoy the magic of dawn! 🌞Many people wake up early to watch the sunrise and drink coffee. In some cultures, people practice yoga or meditate to start their day with peace. Farmers often begin their work at dawn when the coolest temperatures make it easier for plants and animals. Sports enthusiasts also love to jog and run at dawn. It’s a great time to enjoy nature before the busyness of the day starts. 🌺
Dawn In Literature And Art
Dawn has inspired artists and writers for centuries! 🎨In paintings, artists like Claude Monet captured beautiful dawn scenes, showing how the colors change. Many children’s books talk about dawn, like "Goodnight Moon," which shows the transition from night to day. In poetry, poets often write about dawn as a time of dreams and new beginnings, like in William Wordsworth's work. The beauty of dawn makes it a perfect subject for creative minds, bringing joy and wonder! 🌈
Cultural Significance Of Dawn
Dawn holds special meanings in many cultures around the world. 🌄For example, in many religions, dawn is considered a time of hope and new beginnings. In Hinduism, it’s a time for morning prayers. In Japan, people admire the cherry blossoms at dawn. The dawn represents a fresh start, encouraging us to be grateful and to enjoy new opportunities. In literature and stories, dawn often symbolizes hope and the idea of a new adventure waiting for us! 😊
The Role Of Dawn In Ecosystems
Dawn is an important time for many plants and animals! 🌼During dawn, many creatures wake up. Birds start to sing, looking for food and friends. Butterflies flap their wings as flowers bloom. This is when many insects become busy pollinators! Some animals, like rabbits and deer, feel safer venturing out at dawn, avoiding predators. Plants begin to photosynthesize, turning sunlight into energy! Ecosystems thrive because of this daily cycle, making dawn essential for life on Earth! 🦋
Historical Perspectives On Dawn
Throughout history, people have celebrated dawn as a significant time. 🌅Ancient cultures noted sunrise in their calendars and rituals. The Egyptians called it "the hour of the morning." In Greece, people greeted the dawn with festivals! Even today, dawn symbols can be found in flags and literature, reminding us of renewal. Writers like Homer often wrote about the beauty of dawn. As time passes, the appreciation for dawn stays strong, connecting us to our past and to nature! 🏛️
Dawn Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required