Beak Facts For Kids
The beak, or bill, is a hard, pointed mouth structure primarily found in birds and some other animals, playing key roles in feeding, grooming, and communication.
Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
Beaks, also called bills or rostrums, are fascinating structures found mainly on birds! 🦜They come in all shapes and sizes, and they help birds eat, drink, and communicate! Beaks are made of a hard material called keratin, which is similar to our fingernails. There are over 10,000 different species of birds around the world, and they can be found in every continent! From the tiny hummingbird in the Americas to the majestic albatross in the oceans, beaks play a crucial role in a bird's survival. Next time you see a bird, take a close look at its beak!
Gallery of Beak Facts For Kids
Anatomy Of The Beak
A bird's beak has several parts! 🎶The upper part is called the "maxilla," while the lower part is called the "mandible." The tip of the beak can have different shapes depending on the bird's diet. For example, the beak of a parrot is curved for cracking nuts, while the beak of a hummingbird is long and narrow for sipping nectar from flowers. Some birds even have special structures like the "nostrils" on their beaks for breathing. Understanding the anatomy helps us know how birds use their beaks to thrive in their environments.
Evolutionary History
Beaks have a long and interesting evolutionary history. 🦖Scientists believe that birds evolved from small, feathered dinosaurs around 150 million years ago. Fossils show that some dinosaurs, like the "Archaeopteryx," had beaks, too! Over time, different bird species adapted their beaks to suit their environments and diets. For instance, finches on the Galápagos Islands have varied beak shapes to help them eat different foods. Charles Darwin studied these finches in the 1830s, leading to important discoveries about evolution! Beaks tell us a lot about how life on Earth has changed over millions of years!
Functions Of The Beak
Beaks serve many important functions! 🌍First, they help birds eat by breaking down food. For example, woodpeckers use their strong beaks to chisel into trees to find insects. Beaks are also crucial for grooming—birds clean their feathers using their beaks. Communication is another function; some birds use their beaks to make noises or show affection. Additionally, beaks are used for building nests by gathering twigs and leaves. Clearly, beaks are not just for eating; they help birds with many everyday activities!
Beak-related Behaviors
Birds display many amazing behaviors related to their beaks! 💚For instance, some birds use their beaks to coat feathers with oils, keeping them waterproof and clean. Others, like the African Grey Parrot, can mimic human speech using their beaks! Courtship displays often involve beak movements, where male birds show off bright beaks to attract females. Some species even use their beaks in playful ways, like tossing objects or playing games. Observing these behaviors teaches us more about the intelligence and social lives of birds. Every connection to their beaks reveals fascinating insights!
Adaptations For Feeding
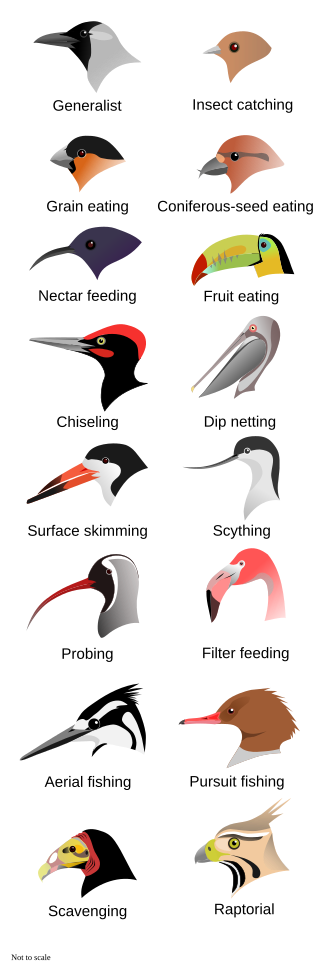
Birds have developed special adaptations in their beaks for feeding! 🦩For example, the seed-eating finch has a thick, strong beak to crack open hard seeds. Nectar-feeding birds, like the hummingbird, have elongated beaks to sip nectar from flowers. Some birds, like pelicans, possess pouch-like beaks for catching fish. Even penguins have beaks that help them catch slippery fish underwater! Adaptations allow birds to eat various foods, helping them survive and thrive in different habitats. This is why studying beaks is essential for understanding bird diversity and ecology!
Beak Variations Across Species
Birds have amazing beak variations! 🌈For instance, the African Spoonbill has a flat, spoon-shaped beak to help it filter food from water. In contrast, the eagle has a sharp, hooked beak perfect for tearing meat. Flamingos have long, curved beaks that allow them to eat tiny shrimp in muddy waters. Even the smallest birds, like the bee hummingbird, which is just 2.2 inches long, have uniquely shaped beaks. Scientists study these variations to understand how birds have adapted to their environments. This diversity helps create a balanced ecosystem!
Conservation Of Beak Diversity
Conserving beak diversity is crucial for our planet! 🌳Many bird species face threats like habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Protecting their environments ensures that birds can continue evolving diverse beaks that suit special diets. Conservation efforts help maintain healthy ecosystems, allowing birds to thrive. Organizations, such as the Audubon Society, work hard to create safe spaces for birds and educate people about their importance. By learning about beaks and their ecological roles, we can join in the effort to protect these amazing creatures and celebrate the diversity of their world!
Comparison With Mammalian Snouts
Did you know that birds' beaks are quite different from mammalian snouts? 🐶While both structures help animals eat, they are made of different materials. Beaks are hard and made from keratin, while mammalian snouts have flesh and bones. Beaks can be more specialized for particular diets, while mammalian snouts may have broader functions, like smelling and tasting. For example, dogs have strong snouts for sniffing out scents, while birds have specialized beaks for picking food. Learning about these differences helps us appreciate the uniqueness of animal adaptations!
Beak Size And Shape Relationships
Did you know that beak size and shape can tell us what a bird eats? 📊Birds with larger, stronger beaks, like the toucan, can eat bigger fruits, while smaller beaks work best for tiny insects. The famous Galápagos finches have different beak shapes depending on their food source! Finch species with wide beaks thrive on seeds, while those with narrow beaks catch insects. Scientists study these relationships to learn how environments influence bird evolution. By exploring beak sizes and shapes, we gain insight into the wonderful world of birds!
Beak Coloration And Its Significance
Beaks can come in different colors, and these colors often have special meanings! 🟡For example, vibrant beak colors may help attract mates. Male birds might show brighter beaks to impress females during courtship. Some birds, like the flamingo, even change color based on their diet! The more shrimp they eat, the pinker their beaks become! Additionally, dark-colored beaks can help with heat regulation in hot climates. Birdwatchers love to admire the colorful variations and understand their significance in communication and attraction. Beaks are not only functional but beautiful, too!
Beak Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required