Neutron Facts For Kids
Neutrons are neutral subatomic particles found in atomic nuclei, playing a significant role in nuclear stability and reactions.
Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
Neutrons are tiny particles that live inside atoms, which are the building blocks of everything around us! 🏠🔬 While they are similar to protons, the other main particle in atoms, neutrons have no electric charge. This means they are neutral, hence the name "neutron!" Neutrons help hold the nucleus of an atom together with protons. An interesting fact is that neutrons exist in all elements except hydrogen, which has just one proton and no neutrons. Neutrons play a vital role in the world of science, helping us understand everything from chemistry to energy! ⚛️
Gallery of Neutron Facts For Kids
Properties Of Neutrons
Neutrons have unique properties, making them essential in the atomic world! 🪐They have no electric charge, which is why they can easily fit with positively charged protons in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are slightly heavier than protons and have a mass of about 1.008664 atomic mass units (amu). Each neutron has a mean lifetime of about 14 minutes when outside the nucleus! 🕒This means if you take a neutron out of an atom, it will eventually decay into a proton and an electron. Neutrons also help keep the atom stable by balancing the positive charge of protons. ⚖️
Future Research On Neutrons
Scientists are always looking for new ways to study neutrons and their properties! 🔍Future research might help us harness neutrons for cleaner energy sources or advance medical treatments. Some researchers are also exploring how neutrons can help us create super materials for technology. For instance, neutron technology can help build smarter batteries or stronger materials for airplanes! ✈️ The potential to learn more about neutrons can change the way we live and solve big problems. Who knows what exciting discoveries are yet to come? 🌈
History Of Neutron Discovery
The neutron was discovered by a British scientist named James Chadwick in 1932. Chadwick worked at the University of Cambridge and made this exciting discovery while studying atomic structure. 🧑🔬 At that time, scientists knew about protons and electrons, but neutrons were a mystery! Chadwick's experiment involved bombarding beryllium with alpha particles, which led him to find neutrons. His discovery earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1935! 🏆This was a big breakthrough in understanding atoms, and it opened the door for many new scientific advances.
Safety And Neutron Radiation
While neutrons are fascinating, they can also be dangerous! ⚠️ Neutron radiation can happen when neutrons escape from a nuclear reactor or during certain types of nuclear reactions. This radiation can penetrate matter and damage cells in our bodies. That's why scientists must follow strict safety rules when working with neutrons! 🛡️ Special shields made from materials like water or concrete are used to protect people from neutron exposure. Always remember, safety first when working with anything that involves radiation! 🛑
Neutron Sources And Detection
Scientists have to produce neutrons in special places called neutron sources. 🔬One common type is a research reactor that uses nuclear fission to create neutrons. For example, the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee is a well-known facility for neutron science! To detect neutrons, scientists use devices called neutron detectors. Some common types of detectors include plastic scintillators and Helium-3 detectors. These tools help researchers measure and study neutrons, making sure they can understand their properties and uses accurately! 📊
Neutrons And Atomic Structure
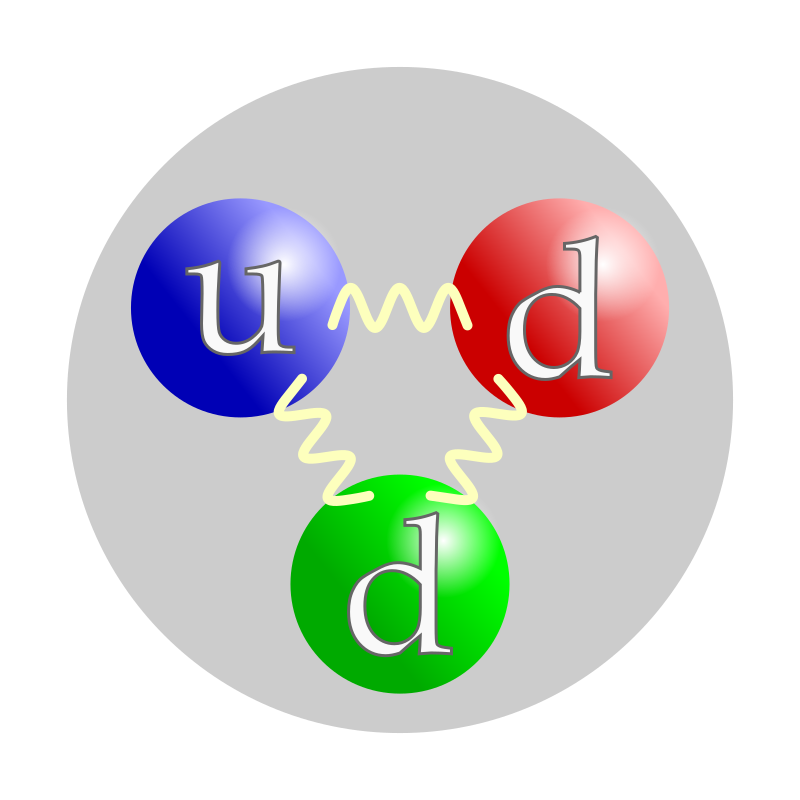
Inside an atom, neutrons are found in the nucleus along with protons. This nucleus is at the center of the atom and is incredibly small compared to the entire atom. 🔎In fact, 99.9% of the atom's mass comes from the nucleus! The number of neutrons in an atom helps define what element it is. For example, carbon typically has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, while carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons. The different numbers of neutrons give rise to different isotopes, which have different properties! 🧬
Neutrons In Nuclear Reactions
Neutrons play a big role in nuclear reactions, where atoms can give off energy. When a neutron strikes the nucleus of an atom, it can cause the atom to become unstable! ⚡This can lead to a process called fission, which is how nuclear power plants create electricity. In fission, a heavy atom (like uranium) splits into smaller atoms, releasing a lot of energy! 🏭Neutrons can also be used in fusion, where light atoms (like hydrogen) combine to form heavier ones, releasing even more energy. This is what powers the sun and other stars! 🌟
Applications Of Neutrons In Science
Neutrons are incredibly useful in science! 🌐They are used in techniques like neutron scattering, which helps scientists study the structure of materials. For instance, scientists can learn about the properties of metals, polymers, and even biological molecules! 🦠By analyzing how neutrons interact with materials, researchers can understand their behaviors better. Neutrons are also crucial in medicine, as they are used in radiation treatments for cancer. 🏥This means they help doctors find and destroy cancer cells in our bodies!
Neutron Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required