Kelvin Facts For Kids
Kelvin is a thermodynamic temperature scale where absolute zero is defined as 0 K, and it is widely used in scientific applications.
Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
The Kelvin scale is a special way to measure temperature! 🌡️ It starts at absolute zero, which is -273.15 degrees Celsius! Brrr! The Kelvin scale is used mostly in science because it helps scientists understand really cold things and really hot things. The symbol for Kelvin is "K." Unlike other temperature scales, Kelvin doesn’t use negative numbers. It is named after a very smart man named Lord Kelvin, who helped us understand heat and energy. So, when you hear "Kelvin," think about the super cool and super hot temperatures that scientists study! 🔍
Gallery of Kelvin Facts For Kids
Definition And Units
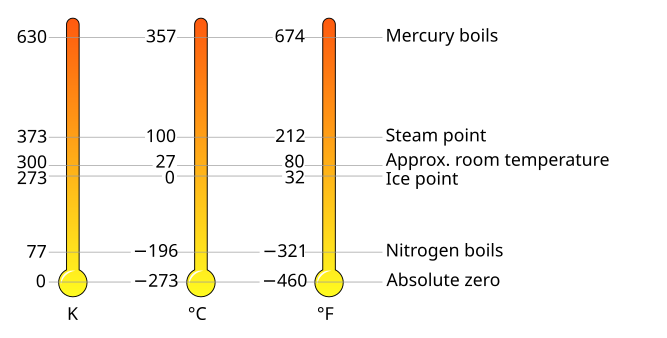
The Kelvin scale measures temperature using "Kelvins," not degrees. For example, 0 K is absolute zero, where all movement stops, and water freezes at 273.15 K. 💧This means that in Kelvin, the water freezes at 273.15, and it boils at 373.15 K! The Kelvin scale uses a neat system where every increase by 1 K is the same as increasing 1 degree Celsius. So, it helps scientists keep everything very clear and straightforward when they study temperature! 📏
Applications Of Kelvin
The Kelvin scale is super important in many areas of science! 🌍It helps scientists study anything from melting ice in Antarctica to the hottest stars in outer space! 🌌It is also used in chemistry for reactions that involve heat and energy. Engineers use Kelvin when creating things like airplanes and robots! Even climate scientists look at Kelvin to see how temperatures change on Earth. So whenever there’s a temperature change in the universe, scientists are often using the Kelvin scale to understand it! 🔭
History Of The Kelvin Scale
The Kelvin scale was created in 1848 by a famous scientist named William Thomson, who became known as Lord Kelvin. 🌌He wanted to find a temperature scale that didn’t have negative numbers. He based it on the Celsius scale but moved the starting point to absolute zero – the coldest temperature possible, where everything stops moving! This change made it easier for scientists to measure really low and high temperatures. In 1954, the Kelvin scale was officially adopted, making it a key part of science around the world, especially in physics and chemistry! 🔬
The Kelvin Scale In Science
In science labs, the Kelvin scale is often used for experiments! 🔬Physicists, chemists, and even astronomers rely on it. For example, when scientists study the temperature of stars, such as the Sun, they use Kelvin because they’re extremely hot! 🌞The Kelvin scale is also essential for studying gases and liquids at different temperatures. By using Kelvins, scientists can make precise calculations and predictions about how materials will behave. The Kelvin scale helps researchers unlock many mysteries of our universe! 🌌
Interesting Facts About Kelvin
Here are some super cool facts about Kelvin! 🥳Lord Kelvin was actually a physicist and mathematician from Scotland! Did you know that in liquid helium, you can reach temperatures below 1 K? 🥶Also, 1 K is the same as 1°C when measuring temperature changes, making it very user-friendly! 🌍Scientists can use the Kelvin scale to measure the temperature of stars billions of light-years away! 🌌Isn’t that amazing? Lastly, Kelvin is a part of the International System of Units (SI), making it an important standard worldwide! 🌏
Limitations And Misconceptions
While the Kelvin scale is helpful, there are some limitations! 🔍One common misconception is that absolute zero can be reached. In reality, scientists can get very close, but they can't reach it! Also, many people confuse Kelvin with Celsius and Fahrenheit, thinking they are the same. They are different, as Kelvin is always positive, whereas Celsius and Fahrenheit can be negative. 🌡️ Understanding this will help you use temperature scales correctly in science! Always remember to think of the Kelvin scale as a fantastic scientific tool! 🛠️
Famous Experiments Involving Kelvin
One well-known experiment using the Kelvin scale is the "Cryogenic Experiment" which cools materials to super-low temperatures close to absolute zero! ❄️ Scientists like Louis Essen used Kelvin to create atomic clocks, making timekeeping incredibly accurate! ⏰Another exciting experiment was the discovery of Bose-Einstein condensates in 1995 by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman. They cooled atoms to near absolute zero, creating a new state of matter! These experiments have helped us understand how matter behaves in extreme conditions! 🔬
Conversion Between Kelvin And Other Temperature Scales
Converting between Kelvin and other temperature scales is easy! 😊To change Celsius (°C) to Kelvin (K), just add 273.15. For example, if it’s 25 °C outside, it’s 298.15 K! 🔄To convert Kelvin back to Celsius, just subtract 273.15. Kelvin works with Fahrenheit (°F) too, but it takes a little more math. To convert Kelvin to Fahrenheit, multiply by 1.8 and then subtract 459.67. Remember to always double-check your math; accuracy is key in science! 📚
Kelvin Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required