Facts for Kids
Entropy in physics quantifies the degree of disorder or randomness in a system and is a central concept in thermodynamics.
Overview
What Is Entropy
Measuring Entropy
Entropy In Chemistry
Applications Of Entropy
Entropy And The Universe
Entropy In Everyday Life
Entropy And Information Theory
The Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Understanding Entropy Through Examples
Inside this Article
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Ludwig Boltzmann
Thermodynamics
Climate Change
Communication
Technology
Chemistry
Big Bang
Paint
Time
Did you know?
🌌 Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system.
⚛️ The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the total entropy of an isolated system can only increase over time.
⏳ In thermodynamic processes, entropy tends to move from lower to higher values.
🌍 The concept of entropy applies to various fields, including chemistry, psychology, and information theory.
🌡️ When heat is transferred in an irreversible process, entropy increases.
🔄 Entropy is often thought of as the arrow of time; as time progresses, entropy increases.
⚙️ In a reversible process, entropy remains constant, while in irreversible processes, it increases.
💡 A higher entropy state is generally considered less useful for performing work.
🔬 In statistical mechanics, entropy quantifies the number of microscopic configurations that correspond to a thermodynamic system's macroscopic state.
🌠 The entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero at absolute zero temperature, which is described by the Third Law of Thermodynamics.
Introduction
It helps us understand how energy and order work in the universe. Think of it like a messy room. When everything is tidy, it has low entropy. When toys and clothes are scattered everywhere, it has high entropy! This means that things tend to get messier over time, just like how ice melts into water. Entropy is linked to something called the Second Law of Thermodynamics, which tells us that energy moves around and spreads out. So, learning about entropy helps us see how nature loves to be a little messy! 🌌
What Is Entropy?
When you have a neat stack of blocks, there’s low entropy because there’s only one way to stack them. But if you dump them out in a pile, you can arrange them in many different ways! This means there is higher entropy. Some scientists, like Ludwig Boltzmann, helped us understand entropy better. ⚗
️ So, entropy tells us how organized or disorganized things are in nature!
Measuring Entropy
By examining the different arrangements of particles, scientists can calculate how much entropy is in a system! This is important for everything from studying engines to understanding climate change. So, measuring entropy is like being a detective in science! 🕵
️♂️
Entropy In Chemistry
When sugar dissolves in water, it spreads out and increases entropy because its particles move around more. A solid has low entropy, while a gas has high entropy because gas molecules move freely! This is why steam from your hot soup spreads out into the air! 🍲
Chemists often measure entropy to predict how reactions happen. Remember, the world of chemistry loves movement and change, making it a great place to see entropy in action every day!
Applications Of Entropy
For example, in biology, we can see how living organisms maintain order by using energy. Plants take in sunlight (energy) and create food, which helps keep low entropy! 🌱
In technology, engineers consider entropy when designing efficient machines and computer programs. Entropy even helps in understanding natural disasters like fires and floods. It shows us how order changes to chaos and helps solve different problems! ⚙
️
Entropy And The Universe
Everything in space, like stars and planets, experiences entropy. The universe started with low entropy during the Big Bang, but as time goes on, entropy increases. 🌟
For example, as stars burn out, they explode and scatter all their materials into space, increasing entropy! Scientists believe that eventually, the universe will reach a state where everything is evenly dispersed, called "heat death." So, understanding entropy helps us learn more about how our fascinating universe works! 🚀
Entropy In Everyday Life
Imagine a warm pizza on a table. When it's fresh out of the oven, it's organized and hot. But as it sits, it cools down and the heat spreads out. The pizza gets colder, increasing entropy! Another example is when you mix two different colors of paint. 🎨
At first, they are separate, but as you mix them, they spread out and create a new color with higher entropy. These examples show how we experience entropy in our daily lives every day!
Entropy And Information Theory
Information theory studies how to send and receive messages. The more uncertain a message is, the higher its entropy! For example, if I say, “I will choose a toy,” it has low entropy because you can guess easily. But if I say, “I will choose one of 20 toys,” it has higher entropy, making it harder to guess! 🧸
Understanding this helps computer scientists improve technology and communication, like sending secret codes or safe messages across the internet!
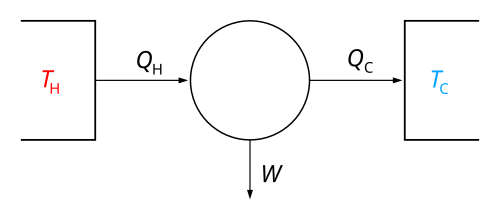
The Second Law Of Thermodynamics
This means that energy will spread out and that things will become more and more disorganized unless we put in energy to keep them organized. For example, when you put ice in warm water, the ice melts, and energy spreads out. This is why your cold drink gets warm! 🥤
It reminds us that energy likes to move around, which is very cool—just like nature’s way of creating change!
Understanding Entropy Through Examples
Think about a bag of marbles. If all the red marbles are on one side and all the blue marbles on the other side, that’s low entropy. But when you shake the bag, the marbles mix, and now it has high entropy! This mixing is natural and happens all around us. 🎉
Another example is when you leave a delicious cake out. Over time, it will get stale and lose its shape, showing how higher entropy loves to come into play. Everything tends to become less organized over time!

