Thymus Facts For Kids
The thymus is a small, butterfly-shaped organ that is vital for the development and maturation of T-cells, playing a significant role in the body's immune system.

Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
The thymus is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located right behind your breastbone, in the center of your chest. 🦋It usually weighs about 25 grams in kids and is important for our immune system! 🛡️ The thymus is in charge of helping to create special cells called T-cells, which help protect your body from germs and illness. These T-cells learn to recognize what's “friendly” and what’s “dangerous” to keep you healthy. The thymus is most active during childhood and slowly shrinks as we become adults. Can you believe that it's like a school for immune cells? 📚
Gallery of Thymus Facts For Kids
Thymic Hormones
The thymus releases special chemicals called hormones like thymosin and thymopoietin. 💊These hormones are like teachers, guiding the T-cells as they develop! They help the cells learn how to fight off bad germs and infections, making sure they're ready when needed. 🌟When T-cells are trained correctly, they help you stay healthy. Without these hormones, it would be harder for your body to defend itself!
Thymus And Aging
As we grow older, our thymus gets smaller, like a balloon losing air 🎈! After the age of 25, it shrinks and begins to be replaced by fat. This means the number of T-cells made by our thymus decreases, making it harder for our body to fight infections. 🤒But don't worry! As adults, we still have other parts of our immune system to help protect us. Just like how you learn new things in school, your immune system learns too!
Thymus In Evolution
The thymus is found in many animals, not just humans! 🦁It shows us how important it has been in evolution for keeping creatures safe from infections. Even in fish, birds, and mammals, there are thymus glands that help create immune cells! 🐦Learning about other animals helps scientists understand how our immune systems work. Evolution shows us that having a thymus has helped many species survive over millions of years!
Anatomy Of The Thymus
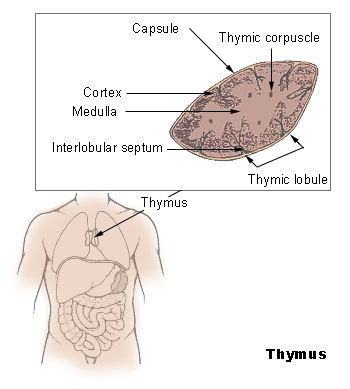
The thymus has two main parts, called lobes. 🤲Each lobe is divided into smaller sections, kind of like the classrooms in a school! The outer part is called the cortex, where T-cells are formed. Inside, there is the medulla, where T-cells mature. The thymus is made of special cells that help these immune cells learn to fight germs. It’s located right under your neck and stays there until you’re about 25 years old, when it starts to shrink and turn into fat! 🧈Amazing, right?
Development And Maturation
The thymus is most important when you are young. 🤗It starts developing during your fetal stage, around the 7th week of pregnancy! Once you are born, the thymus grows quickly until you’re about 12 or 13 years old. After that, it stops growing and begins to shrink. Parents often say kids have great energy—part of that is thanks to the thymus making many T-cells to keep them safe! 🌈This is why early childhood is a magical time for building strong immune defenses!
Function In The Immune System
One of the thymus’s main jobs is to create T-cells, which are a type of white blood cell. 💪These T-cells attack and destroy germs like bacteria and viruses that can make us sick! They also help your body remember these germs so it can fight them better if they come back! The T-cells learn to recognize what belongs in your body and what does not. This helps keep you safe and healthy at all times. Have you ever fought an imaginary monster? That’s what T-cells do in real life!
Diseases Related To The Thymus
Sometimes, things can go wrong with the thymus. One condition is called myasthenia gravis, where the T-cells can mistakenly attack your own muscles, making them weak. 😞Another issue can be thymoma, which is a tumor in the thymus. Both can make it hard for the immune system to work properly. Doctors study these conditions to help people feel better, just like superheroes on a mission! 🦸✨
Research And Future Directions
Scientists are still learning about the thymus and how it works! 🧬New research explores using thymic hormones to help people boost their immune systems or fight diseases. 💡There are also studies looking into ways to help the thymus stay healthier as we age. It’s a fascinating journey of discovery! As scientists unlock more secrets, they hope to make our bodies stronger and protect us better. The future is bright for thymus research! ☀️
Thymus Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required