X-ray Diffraction Facts For Kids
X-ray diffraction is a technique that utilizes X-rays to study the structure of crystalline materials at the atomic level.
Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
X-ray diffraction is a cool science technique used to study materials! 🌍It helps scientists understand the structure of tiny things like crystals, minerals, and even proteins. The name "X-ray" comes from the type of light it uses — something our eyes can't see but that can go through different materials. When X-rays hit a sample, they bounce off in different directions, just like how light bends when it hits glass. 🌈This bending creates a pattern called a diffraction pattern, which tells scientists how the atoms are arranged!
Gallery of X-ray Diffraction Facts For Kids
Challenges And Limitations
Even though X-ray diffraction is super useful, there are some challenges! 😕For example, not all materials form perfect crystals, which makes it hard to get clear patterns. Some samples might also absorb X-rays instead of allowing them to pass through, leading to weak signals. 🌪️ Additionally, complex materials with many components can create complicated patterns that are difficult to interpret. Scientists spend a lot of time figuring out these issues, but they keep improving techniques to overcome these limitations!
History Of X-ray Diffraction
X-ray diffraction was discovered in 1912 by scientists Max von Laue, William Henry Bragg, and his son, William Lawrence Bragg. They were curious about how light interacts with materials. 🌌Max von Laue was from Germany, and the Braggs were from England. They used X-rays on a crystal of copper sulfate and saw patterns! 🔍Their discovery helped them win the Nobel Prize in Physics by 1915! This was a significant moment in science because it opened up new ways to explore materials, making it easier to understand the building blocks of everything around us.
Role In Biology And Medicine
X-ray diffraction is super important in biology and medicine too! 🏥It helps scientists understand how proteins and other biological molecules work. For example, the structure of DNA was discovered using X-ray diffraction by Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins. 🧬Knowing how these structures look helps researchers develop medicines and treatments! X-ray diffraction is also used to study viruses and bacteria, helping doctors create vaccines. So, when someone feels sick, scientists can figure out how to make them better, all thanks to the power of X-ray diffraction!
X-ray Diffraction Techniques
There are several techniques of X-ray diffraction scientists use! One common method is called "single-crystal diffraction." 🔷 This involves shining X-rays on a single crystal and analyzing the resulting pattern. Another technique is "powder diffraction," where scientists use powdered samples instead of whole crystals. This is useful for materials that cannot form large crystals. ☢️ Additionally, there are advanced methods like "synchrotron radiation," which uses super-bright X-rays from a particle accelerator. 💥These techniques allow for more detailed information about materials, leading to better discoveries in science!
Principles Of X-ray Diffraction
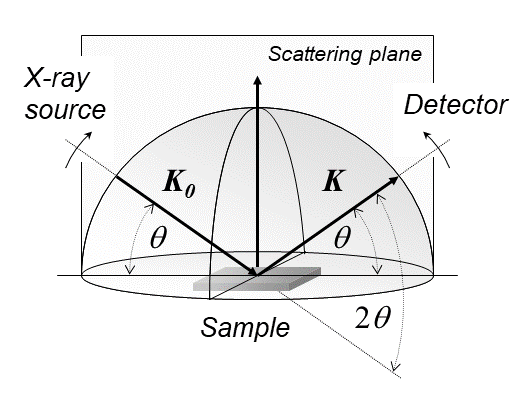
The main idea behind X-ray diffraction is called the "wave-particle duality." 🤔 X-rays behave like both waves and particles. When X-rays hit a crystal, they are scattered or bent. This scattering happens because the atoms in the crystal act like a camera lens, creating a pattern. This process can be explained by something called Bragg's Law. 📏It states that when the angle of X-ray hitting the crystal is right, constructive interference occurs! This results in bright spots on a film or detector, allowing scientists to determine the structure of the material.
Applications In Material Science
Scientists use X-ray diffraction in many areas of material science! 🔬For example, they can identify how minerals are arranged in rocks or how metals are structured. This information is important for building things, like bridges and airplanes. Also, X-ray diffraction helps create stronger materials. For instance, it's used in making high-tech gadgets like smartphones and laptops! 💻This technology can also reveal how different materials behave under various conditions, like temperature changes. Discovering and understanding these structures has allowed us to create new materials that improve our world!
Data Analysis And Interpretation
Understanding X-ray diffraction patterns can be tricky! 🧩Scientists process the patterns using computer programs to turn them into useful information. They analyze the angles and intensities of the spots created by the X-rays. This data tells scientists the distance between atoms and how they are arranged. Knowing how to read these patterns helps scientists identify unknown materials or refine their understanding of known ones! 📊This information can lead to important discoveries, affecting fields like energy, electronics, and medicine.
Future Developments In X-ray Diffraction
The future of X-ray diffraction looks bright! 🌟Scientists are developing new technology to make X-ray beams even brighter and more focused. This will help them study smaller samples and gather more details quickly! 🕒Moreover, researchers are exploring how X-ray diffraction can be combined with other techniques, like electron microscopy, for a better understanding of materials. ⚛️ These advancements might lead to new discoveries in medicine, renewable energy, and nanotechnology! The possibilities are endless, and who knows what exciting things we will learn next!
X-ray Diffraction Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required