Particle Physics Facts For Kids
Particle physics is the branch of physics concerned with the study of the smallest known particles and their interactions.

Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
Particle physics is the study of the tiniest building blocks of our universe! 🌌Did you know everything around us—like trees, animals, and even humans—is made up of particles so small you can't even see them? There are tiny particles called atoms, and these atoms are made of even smaller particles called quarks and electrons! Particle physics helps us understand how everything in the universe works, from the stars in the sky down to the particles that make up a grain of sand. It's like exploring the super-small world and figuring out the secret code of nature! 🔍✨
Gallery of Particle Physics Facts For Kids
Detection Methods
To study particles, scientists need special detectors! 🕵️♂️ These detectors can identify particles that are too small to see. Some detectors use magnetic fields to analyze the charge of particles, like bubble chambers or cloud chambers. Others, like scintillation detectors, register tiny flashes of light when particles pass through them. There are also larger detectors that capture events happening in accelerators, such as the ATLAS and CMS at CERN. With these amazing tools, scientists can understand the mysteries of the universe and investigate the behavior of fundamental particles! 🔦✨
Fundamental Particles
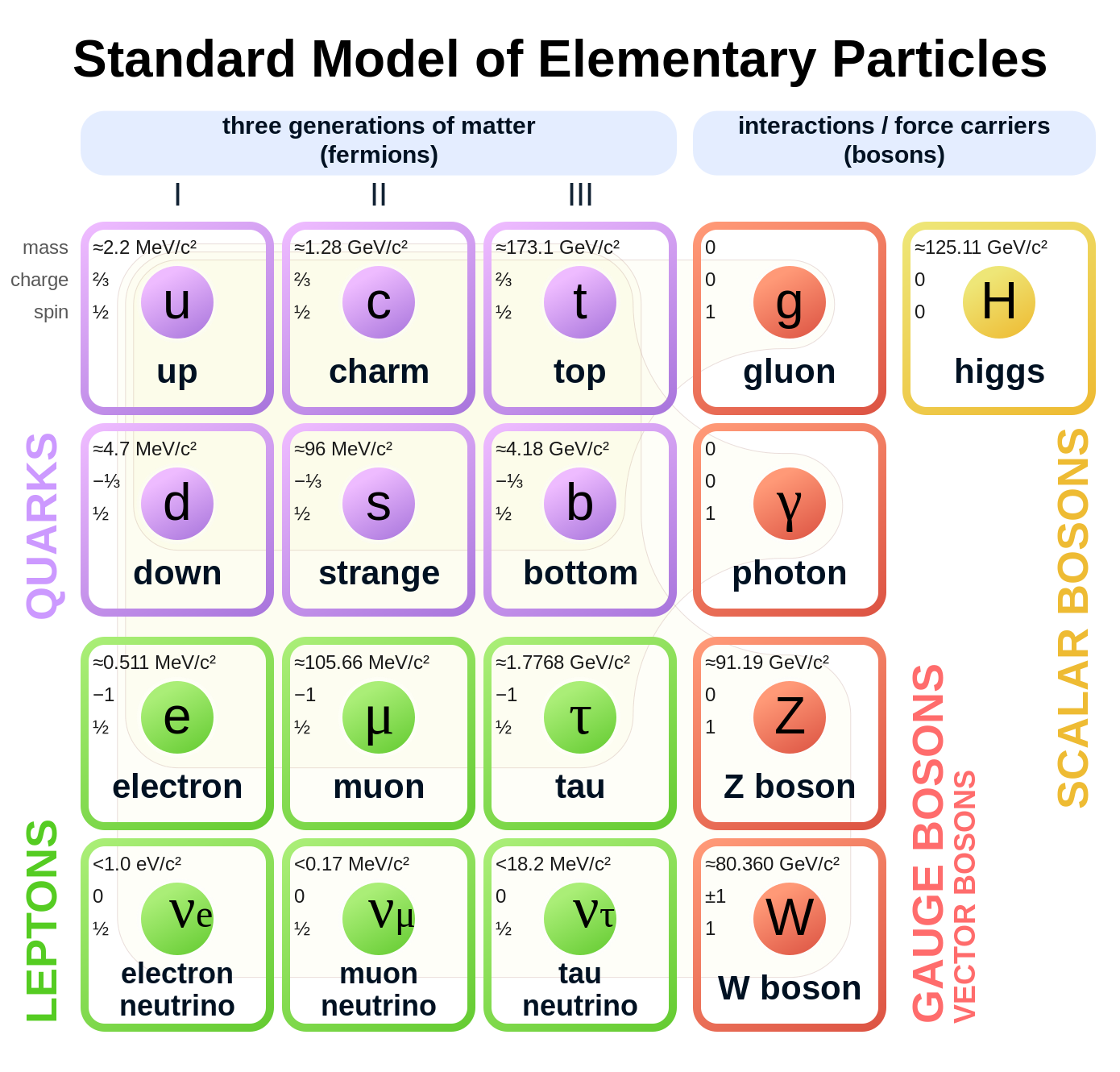
There are two main types of fundamental particles: fermions and bosons! ⚛️ Fermions include quarks and leptons. Quarks are found in the protons and neutrons of atoms, and they come in six “flavors”: up, down, charm, strange, top, and bottom! Leptons, like electrons, are found around the nucleus. Bosons, like the photon (which carries light), act like messengers between particles. The Higgs boson, discovered in 2012, helps explain why some particles have mass! Isn't it cool that all matter is made from just a few types of particles? 🌈
Particle Accelerators
Particle accelerators are machines that speed up tiny particles to amazing speeds! ⚡They help scientists smash particles together to reveal their secrets. The Large Hadron Collider (LHC), located in Switzerland, is the world's largest accelerator—it’s 17 miles (27 kilometers) around! Scientists use accelerators to study fundamental particles and forces. They can create conditions like the ones shortly after the Big Bang, helping us understand our universe better. The LHC is famous for discovering the Higgs boson, an exciting breakthrough in particle physics! 🚀🔍
Forces In Particle Physics
In particle physics, forces help particles interact! There are four fundamental forces: gravity, electromagnetism, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force. 🌍✨ Gravity pulls objects toward each other and keeps us grounded. Electromagnetism interacts with charged particles like electrons. The strong nuclear force holds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus. The weak force helps in certain types of radioactive decay. Each force has its own powerful effects that shape how everything in the universe behaves, from falling apples to swirling galaxies! 🍏🌌
Future Of Particle Physics
The future of particle physics is filled with exciting possibilities! 🌌Scientists are hoping to discover new particles that could explain the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy, which make up most of our universe but remain a secret! There are plans to build even larger particle accelerators to go further into the subatomic world. Some scientists are also exploring different theories that challenge our current understanding, like supersymmetry. As technology advances, particle physics will continue to help us unveil the wonders of the universe. Who knows what we might discover next? 🚀✨
History Of Particle Physics
The journey of particle physics began in the early 20th century! 🚀One of the first scientists to study atoms was Ernest Rutherford in 1911. He discovered the nucleus, the heart of the atom, and proposed that it’s surrounded by electrons. Later, in the 1930s, scientists like James Chadwick found the neutron—another important part of atoms! In 1954, the first particle accelerator was built in the USA, which helped reveal more about these tiny particles. Over decades, theorists and experimenters, including famous scientists like Richard Feynman, made amazing discoveries, paving the way for modern particle physics! 🔬🔭
Applications Of Particle Physics
Particle physics isn't just about studying tiny particles; it has many practical uses! 🌟For instance, the discoveries made in particle physics have led to medical advancements like PET scans, which help doctors see inside our bodies. These scans use particles to detect diseases like cancer. Particle physics also plays a role in developing new materials and technologies, like computer chips! Scientists even study cosmic rays, which are high-energy particles from outer space, to learn more about space weather and protect satellites. Who knew particle physics could be so useful? 💻🩺
Current Research And Discoveries
Today, scientists continue to explore the universe through particle physics! 🚀Researchers are using advanced technologies to search for dark matter—an invisible substance that makes up most of the universe. They study neutrinos, tiny particles that hardly interact with anything, to understand their role in the universe. Moreover, scientists are investigating what happened in the first moments after the Big Bang! Exciting experiments in laboratories worldwide aim to uncover new particles and the mysteries of the universe. Each discovery brings us closer to understanding the fundamental laws of nature! 🔭🌌
Particle Physics Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required