Hydrogen Bond Facts For Kids
A hydrogen bond is an attraction between a hydrogen atom, covalently bonded to an electronegative atom, and another electronegative atom, important for the properties of water and biological molecules.

Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
Hydrogen bonds are super cool! They are like invisible forces that keep molecules together. Imagine you have a magnet that can only stick to metal. In chemistry, hydrogen bonds are like magnets but for tiny particles! 💧They happen when a hydrogen atom, which is part of a larger molecule, gets attracted to another molecule with an electronegative atom, like oxygen or nitrogen. These special bonds help shape important things around us, like water and DNA. So, next time you sip water or think about your favorite animal, remember that hydrogen bonds are working behind the scenes! 🌍✨
Gallery of Hydrogen Bond Facts For Kids
What Are Hydrogen Bonds?
A hydrogen bond is a special type of connection in chemistry! 🤓When a hydrogen atom (H) teams up with an electronegative atom, like oxygen (O) or nitrogen (N), it creates a bond that is weaker than regular bonds. The electronegative atoms are like big friends that pull hydrogen closer! Imagine a game of tag, where oxygen is “it” and hydrogen runs to catch up! Hydrogen bonds can happen between different molecules or even parts of the same molecule. They help keep things connected, just like how friends stick together! 🤝
The Role Of Hydrogen Bonds In Water
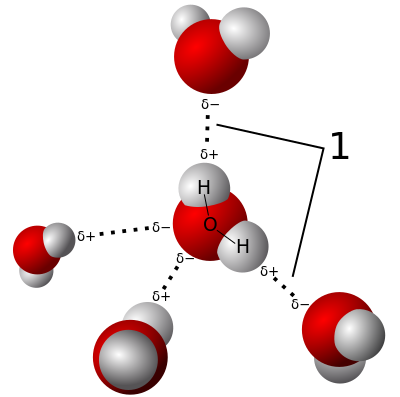
Did you know that water is a magic liquid? 🌊It's made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (H2O). Hydrogen bonds are the reason why water can do amazing things! These bonds make water molecules stick together, which helps create bubbles, raindrops, and even ice! 🧊When water freezes, the hydrogen bonds rearrange, creating a solid that is lighter than liquid water. This is why ice floats! 🎈Without hydrogen bonds, water wouldn’t be as special, and life on Earth would be very different!
Hydrogen Bonds In Biological Molecules
Hydrogen bonds are super important in living things! 🌱In our bodies, they help connect different parts of DNA, the blueprint for life. The bases in DNA, like adenine and thymine, use hydrogen bonds to hold together their unique shapes. This keeps our genetic information safe! 🧬Also, proteins, which help our bodies work, also rely on hydrogen bonds to fold correctly. Without these bonds, life wouldn’t be possible! Imagine a crowded school, where everyone, like hydrogen bonds, helps keep the classroom connected and working together!
Hydrogen Bonds In Crystalline Structures
Did you know that hydrogen bonds can make beautiful crystals? 💎When water freezes into ice, it forms a wonderful crystalline structure! The hydrogen bonds help arrange water molecules in a specific way, creating those sparkling ice cubes we love! ❄️ There are other crystals too, like sugar and salt, that also use hydrogen bonds to form their unique shapes. Crystalline structures are important in nature and tech too. For instance, certain minerals and gems get their beauty thanks to arrangements made by hydrogen bonding! Next time you see crystals, think of their hidden hydrogen bonds making them shine! 🌟
Hydrogen Bond Strength And Characteristics
Hydrogen bonds are like friendly tugs! 🎈They are not as strong as covalent or ionic bonds, with strengths typically between 1-20 kilocalories per mole. When we think of strength, imagine how a balloon feels when you lightly pull on it! 🎈It's easy to stretch but not pop! Hydrogen bonds form when hydrogen is next to electronegative atoms, creating a dipole or imbalance. This makes the hydrogen slightly positive and attracts it to other electronegative atoms. These bonds are short-lived and can break and reform easily. This makes them ideal for many biological processes!
The Importance Of Hydrogen Bonds In Nature
Hydrogen bonds are heroes of nature! 🌳They help shape our environment and make it just right for life. For instance, they allow water to exist as a liquid at Earth’s surface, which is super important for plants and animals. 🌻The hydrogen bonds in water also help transport nutrients in plants through tiny tubes called xylem. In addition, these bonds protect ecosystems, influencing weather patterns and climate. Without hydrogen bonds, Earth would be a very different—and much less lively—place! Thanks to these bonds, we can enjoy beautiful flowers, tasty fruits, and much more! 🍏
Applications Of Hydrogen Bonds In Chemistry
Hydrogen bonds have awesome uses in chemistry! 🧪They help scientists create new materials and study how the building blocks of life work together. For example, in medicine, understanding hydrogen bonds helps create better drugs that can target specific problems in our bodies! 💊In addition, hydrogen bonds allow us to design cool products, like special adhesives that stick well but can still be removed easily. Researching hydrogen bonds can help improve food packaging to keep it fresh! So, hydrogen bonds not only connect molecules, but they also connect scientists with discoveries that help us all!
Comparison: Hydrogen Bonds Vs Other Types Of Bonds
In chemistry, there are different types of bonds. Think of them as building materials! 🧱The strongest bonds are covalent bonds, where atoms share electrons like best friends sharing snacks. Then we have ionic bonds, where one atom gives away electrons, creating a friendship like a big brother and little sister. Hydrogen bonds, however, are like gentle hugs – they are much weaker than both! 🤗They keep molecules together, but they can easily break—perfect for life processes that need flexibility. So remember, each bond has its own special role!
Effects Of Temperature And Pressure On Hydrogen Bonds
Temperature and pressure can change how hydrogen bonds work! ☀️ When it gets warmer, like on a sunny day, the molecules move faster, causing hydrogen bonds to break more easily. This is why ice melts into water! ❄️ Then, when it’s cooler, the molecules slow down, and the bonds can form again. Pressure also plays a role! Imagine squishing a sponge—making it smaller brings the molecules closer, making it easier for hydrogen bonds to form. In nature, this is important for weather patterns and water cycles! 🌧️ Understanding how temperature and pressure affect hydrogen bonds helps scientists predict changes in the environment! 🌍
Hydrogen Bond Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required