Glycerol Facts For Kids
Glycerol, or glycerin, is a sweet, syrupy liquid with three alcohol groups, commonly used in food, cosmetics, and medicines.

Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
Glycerol, also known as glycerin, is a sweet and colorless liquid. 🌈It's found in plants and animals and is often used in foods and medicines. Glycerol is a special type of sugar alcohol, and it has three carbon atoms, making it a triol (which means it has three hydroxyl, or -OH, groups!). It can be used to keep things moist and sweet. 🍭Glycerol is popular around the world, especially in places like the United States 🇺🇸 and Europe 🇪🇺. Many people use it without even knowing, as it’s in so many everyday products!
Gallery of Glycerol Facts For Kids
Physical Properties
Glycerol is thick and sticky, which means it has a high viscosity. 🏺It has a sweet taste, even though it’s not sugar! Glycerol has a boiling point of about 290 degrees Celsius (554 degrees Fahrenheit) and a freezing point of around 17.8 degrees Celsius (64 degrees Fahrenheit). Because it can blend with both water and oil, it’s really good at mixing ingredients. 🚰This makes glycerol useful for many products, like food and cosmetics, to keep them fresh and yummy!
Environmental Impact
Glycerol is generally good for the environment! 🌎Since it comes from plants, it’s a renewable resource, which means we can keep using it without running out. When glycerol is produced from waste during oil extraction, it helps reduce waste and makes the process better for the earth. However, if not managed carefully, producing glycerol can lead to deforestation and land-use changes. 🌱It’s important for companies to be responsible while using glycerol to protect our planet!
Glycerol Derivatives
Glycerol can be transformed into other useful compounds called derivatives! 🔄For example, when glycerol is combined with fatty acids, it forms important substances like glycerol monostearate. These derivatives can be used in foods, cosmetics, and medicines. Some make great emulsifiers, which help mix oil and water together. Others are used for making plastics and biodiesel! 🌱Glycerol derivatives show how this simple compound can be turned into many useful products for our world!
Uses In Food Industry
In the food industry, glycerol acts as a sweetener and moisture-retaining agent. 🍰It helps keep things moist in foods like cakes and candies. It’s often found in low-fat and sugar-free products because it adds sweetness without calories! Glycerol also helps keep fruits and vegetables fresh longer. 🍓You might find it in ice creams, sauces, and even some beverages. It’s like a magic ingredient that helps foods taste better and last longer!
Production And Synthesis
Glycerol is mainly made from vegetable oils and animal fats. 🌿🐄 The process of making glycerol begins by breaking down triglycerides, which are fats found in oils. This can be done using heat and chemicals to separate the glycerol from fatty acids. Glycerol can also be made from sugar in a lab, through a fermentation process. 🍽️ Some common sources of glycerol are soybeans, palm oil, and even olive oil!
Health Effects And Safety
Glycerol is safe for most people when used properly! 🎉However, consuming too much glycerol can lead to stomach upset and diarrhea. It’s not toxic, but moderation is key! Some people may have allergies or sensitivities, so it’s always important to check if you’re not feeling well after using products containing glycerol. Always ask your doctor if you have any questions about using glycerol in medicines or skin care. Staying informed keeps you safe! 👍
Chemical Structure Of Glycerol
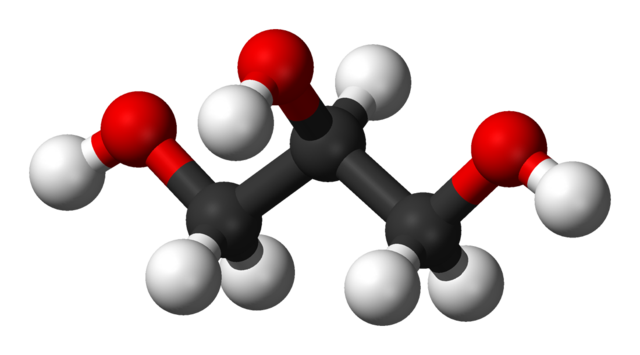
The chemical formula of glycerol is C₃H₈O₃. 🔬This means there are three carbon (C) atoms, eight hydrogen (H) atoms, and three oxygen (O) atoms. Each of the carbon atoms is connected to a hydroxyl group (-OH). This special structure gives glycerol its unique properties. When you think of glycerol, imagine a fun molecule shaped like a Y! ✨The hydroxyl groups make it a great moisturizer, which is why it’s in lotions and creams.
Role In Biology And Metabolism
Did you know that our bodies can create glycerol? 🧬Glycerol is made when our bodies break down fats and sugars during metabolism. It can be used for energy or for making new fats. Glycerol helps store energy and is important for keeping our bodies functioning smoothly. Our liver is the main place where glycerol is produced, and it plays a key role in how we balance our energy needs. 🥦So, the next time you eat, remember how important glycerol is for your body!
Applications In Pharmaceuticals
Glycerol is very important in hospitals and pharmacies! 💊It’s often used in cough syrups and medicines to help patients feel better. Glycerol can help dissolve other medicines, making them easier to swallow. It also acts as a humectant, which means it helps keep the throat moist. Because it is gentle and not irritating, it’s used in many baby and children’s medicines, too! 👶So, if you ever take medicine that tastes sweet, it might just have glycerol in it!
Glycerol In Cosmetics And Personal Care
Glycerol is a superstar in the world of beauty and personal care! 💄It can be found in lotions, creams, shampoos, and soaps. Its moisturizing properties help keep our skin feeling soft and smooth. Glycerol attracts water to the skin, preventing dryness. 🌊Many cosmetic companies love it because it helps products apply easily and makes skin feel great! Since it’s gentle, glycerol is good even for sensitive skin, making it a perfect ingredient for everyone!
Glycerol Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required