Gallium Nitride Facts For Kids
Gallium nitride is a wide bandgap semiconductor with high efficiency and power capabilities, commonly used in electronics and LED technologies.
Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
Gallium nitride (GaN) is a special material that is used in electronics and is very important for our technology! 🌟This material is made from two elements: gallium, which comes from a blue metal found in places like France and Germany, and nitrogen, which we find in the air around us. GaN is cool because it can handle a lot of power and heat, making it perfect for gadgets like smartphones and LED lights. 📱💡 Scientists started studying it in the 1990s, but now it's a star in the world of electronics!
Gallery of Gallium Nitride Facts For Kids
Synthesis Methods
There are different ways to create gallium nitride. One popular method is called metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). 🌬️ In this technique, a gas containing gallium and nitrogen is heated up and deposited onto a surface to grow GaN crystals. Another method is molecular beam epitaxy (MBE), which also helps make high-quality GaN layers! Both methods help scientists create perfect GaN for all our electronic needs, making them very important in labs around the world! 🏭
Chemical Properties
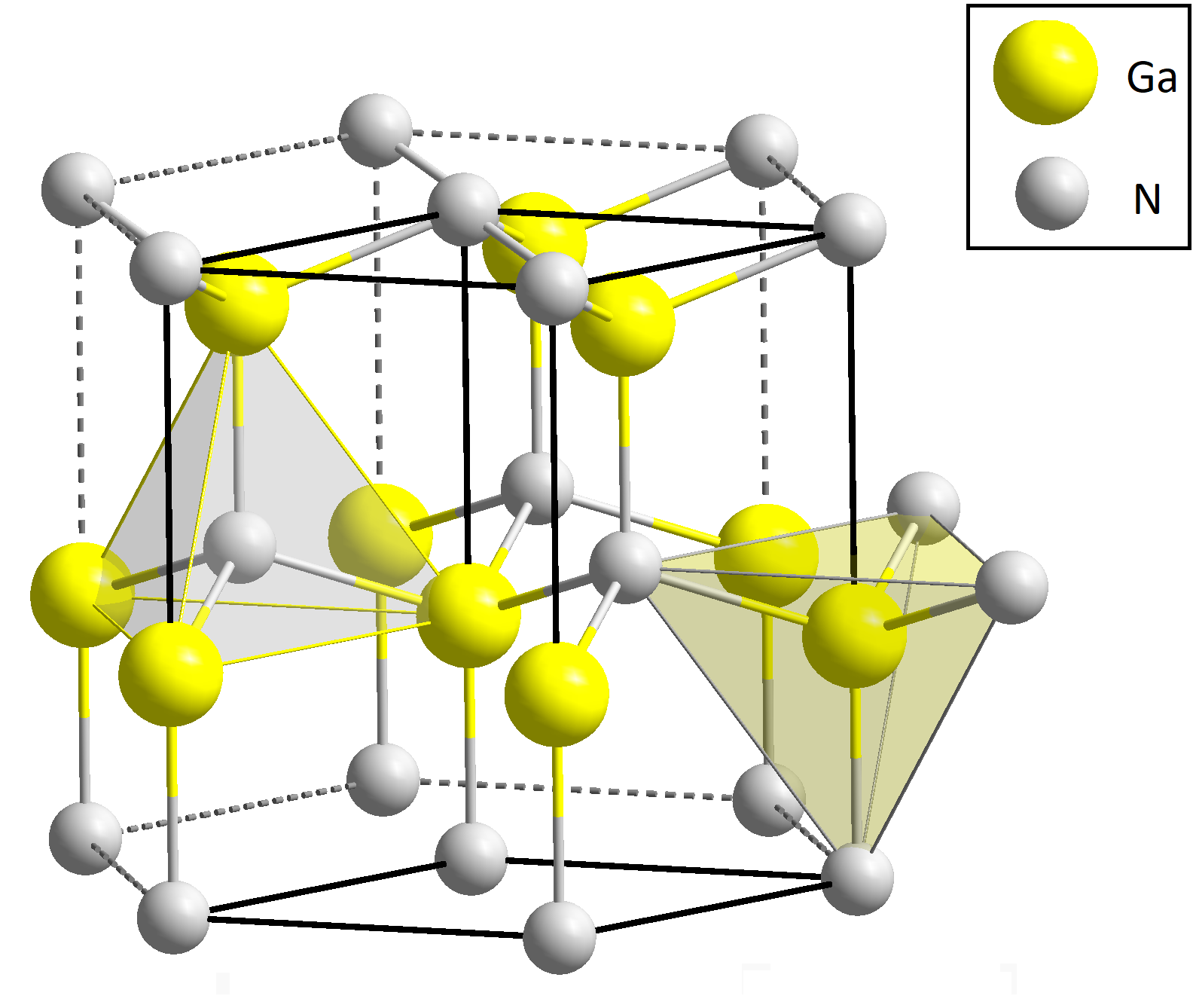
Gallium nitride has a unique chemical structure. 🧪It combines gallium (Ga) with nitrogen (N) to form a compound. GaN is a semiconductor, which means it can conduct electricity under certain conditions, just like silicon. It also has a bandgap of 3.4 electron volts (eV), which is higher than silicon’s 1.1 eV! This means GaN can work at higher temperatures and voltages, making it very efficient. 🌡️ Furthermore, GaN is very stable and can resist heat, which is why we use it in many electronic devices! 🔋
Physical Properties
This material is often found as a shiny, crystal-like solid. 💎GaN is hard and has a high melting point of about 1,600 degrees Celsius (2,912 degrees Fahrenheit), which makes it super strong and durable! 🌞Its physical properties help it perform well in different environments. GaN crystals can be grown in various forms, and they are usually blue or yellowish in color. The unique ability of GaN to emit light makes it essential for creating bright and colorful screens on your tablets and TVs! 📺✨
Historical Development
Gallium nitride was first made in a lab in the 1970s by scientists like Dr. John R. Shealy and Dr. H. Paul Marshall. 👩🔬👨🔬 It wasn't until the 1990s that researchers discovered how to use it for bright blue LEDs. 💙This was super exciting because before that, making blue light was really hard! In 1994, Shuji Nakamura successfully created the first high-brightness blue LED using GaN. His invention helped revolutionize the lighting and display industries, showing just how special this material can be! 🏆
Comparison With Silicon
Silicon has been the go-to material for electronics, but gallium nitride offers some great advantages! 😃While silicon can handle temperatures of about 150 degrees Celsius (302 degrees Fahrenheit), GaN thrives at much higher temperatures, around 600 degrees Celsius (1,112 degrees Fahrenheit). Additionally, GaN is more efficient in turning electricity into light, which is why it’s used in bright LEDs. 🌟So, even though silicon is popular, GaN is like the new superhero in the electronics world, making devices faster and better! 🦸♂️
Role In Renewable Energy
Gallium nitride is very important for renewable energy! 🌍It helps make solar panels and wind turbines more efficient. 🌞💨 GaN technology allows these energy sources to convert sunlight and wind into electricity with less energy loss. For example, GaN-based devices can manage the power used in solar energy systems, ensuring that we get the most out of every ray of sunshine! This means that GaN is not just about gadgets; it's also about helping our planet! 🌱
Future Trends And Research
The future of gallium nitride is super exciting! 🔮Researchers are looking for ways to make GaN even better. They want to create tiny GaN devices that can be used in new technologies like 5G and smart homes. 🏡With GaN, we might have faster internet and smarter gadgets! Plus, scientists are exploring how to use GaN for better solar energy systems and electric vehicles! 🚀The possibilities are endless! Soon enough, we might see gallium nitride powering our world in amazing ways! 🌈
Applications In Electronics
Gallium nitride plays a HUGE role in electronics nowadays! 💻It is used in devices like smartphones, tablets, and computers to help them run faster and use less energy. One major application is in power converters, which help change electricity from one form to another. GaN can also be found in chargers; they improve charging speeds and efficiency! ⚡In addition, GaN helps create high-voltage devices that are used in electric cars, making them more efficient and better for the environment! 🚗
Gallium Nitride Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required