Brahmaputra River Facts For Kids
The Brahmaputra River is one of the major rivers in South Asia, renowned for its vast length, ecological diversity, and cultural importance.
Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
The Brahmaputra River is one of the longest rivers in the world, measuring about 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles)! 🌊It flows through three countries: Tibet in China, India, and Bangladesh. The river starts in the Himalayas and moves through beautiful landscapes. It is an important source of water for millions of people and is known as the "Brahmaputra" in India and Bangladesh, while in Tibet, it is called "Yarlung Tsangpo." The river is famous for its powerful flow and is an exciting place for adventure seekers! 🚣♂️
Gallery of Brahmaputra River Facts For Kids
Biodiversity
The Brahmaputra River is home to many plants and animals! 🌱🐒 In the river, you can find fish like Rohu and catfish. On its banks, you may see endangered animals like the one-horned rhinoceros and the Gangetic dolphin. The wetlands along the river are terrific places for birds, including cranes and herons, making this area a real treasure for nature lovers. 🌿The diverse habitats support various species, showing just how important the river is for amazing wildlife!
Economic Importance
The Brahmaputra River is vital for the economy of the regions it flows through. 🚜Farmers use the river's water for irrigation to grow rice, jute, and tea. Additionally, the river supports fishing, which is a critical source of protein for many people. Transportation is another important feature of the river! Boats carry goods and people, making trade easier between cities. The river helps create jobs and contributes to the livelihood of many communities, showing how important it is for everyday life. 💰
Conservation Efforts
Many organizations and communities are working together to conserve the Brahmaputra River. 🌱They are planting trees to restore the forest along its banks, helping reduce pollution and erosion. Communities are also promoting better waste management practices to keep the river clean. Environmental education programs teach people about the importance of protecting this amazing natural resource. By working as a team, they hope to ensure that the Brahmaputra remains healthy for future generations, supporting both nature and people! 🤝
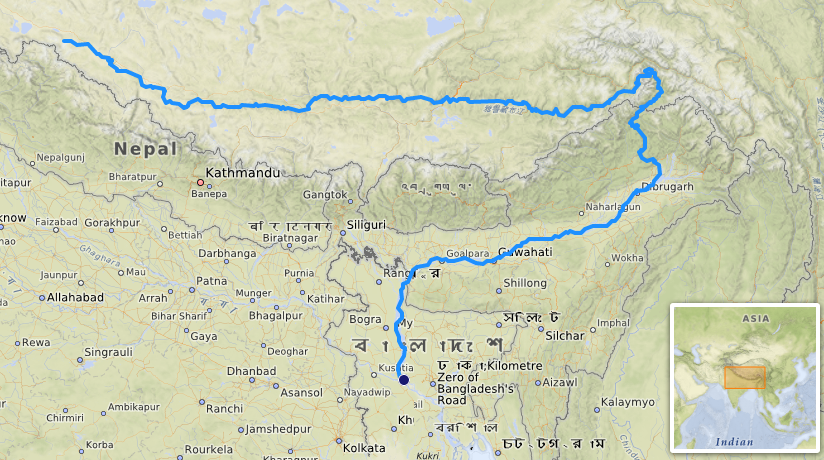
Geography And Course
The Brahmaputra River begins in Tibet, at a high altitude of about 5,000 meters (16,404 feet) 📍. It flows east through the stunning Himalayas, cutting through valleys and mountains. After that, it changes direction, traveling south into India, especially through the northeastern states like Assam and Arunachal Pradesh. Eventually, it flows into Bangladesh, where it merges with the Ganges River and then empties into the Bay of Bengal. Along its journey, the river passes through beautiful towns and villages, providing homes and resources for people living nearby. 🏞️
Cultural Significance
The Brahmaputra River holds great cultural importance in India and Bangladesh. 🕌People celebrate festivals like "Bihu" in Assam, which involves dances and songs honoring the river. The river is also mentioned in ancient scriptures and has a special place in the hearts of many. Communities depend on it not just for food and water, but also for religious practices. People often worship the river, believing it brings good fortune and prosperity! 🌟
Hydrology And Climate
The Brahmaputra River flows through regions with different climates. ❄️ In the Himalayas, the weather is cold, while in Assam, it gets warm and humid, with lots of rain! The river experiences seasonal changes. During the monsoon season (June to September), it can swell, causing floods. In these months, the river gets super powerful! But in winter, the flow slows down. 🌧️ The river is fed by rain and melting snow from the mountains, making it an essential water source for agriculture and homes.
Historical Significance
The Brahmaputra River has played a historical role for thousands of years! 🏺Ancient travelers used it as a trade route, sharing goods and ideas between cultures. Archaeological sites near the river uncover information about past civilizations, like the "Mikir Hills." The river has also been a witness to many historical events and is often mentioned in stories and legends. Its rich history helps people understand how intertwined life is with this incredible river. 📜
Environmental Challenges
Although the Brahmaputra River is beautiful, it faces many environmental challenges. 🌍Pollution from factories and waste can harm the water quality. Additionally, climate change leads to extreme weather, causing floods or droughts, which disrupts the lives of people and wildlife. The deforestation along its banks can lead to soil erosion, making the river less healthy. People and organizations are working hard to tackle these issues to protect the river and its precious ecosystem! ⚠️
Tributaries And Watershed
The Brahmaputra has several tributaries that help it grow bigger and stronger! 🌊Some of the most notable tributaries include the Teesta, Manas, and Subansiri rivers. These smaller rivers bring water, and nutrients, and create an extensive watershed area around the main river. This interconnected system is essential for agriculture, wildlife habitats, and maintaining the overall health of the river. The watershed plays a crucial role in collecting rainwater and melting snow, ensuring the river flows steadily throughout the year.
Did you know?
🌊 The Brahmaputra River is approximately 2,880 kilometers long, making it one of the longest rivers in the world.
🏞️ It flows through three countries: Tibet (China), India, and Bangladesh.
🌧️ The river has a significant monsoon influence, leading to heavy seasonal flooding in certain areas.
🏙️ Major cities along the Brahmaputra include Guwahati in India and Dhaka in Bangladesh.
🐟 The river is home to diverse aquatic life, including the endangered Ganges river dolphin.
📈 The Brahmaputra is vital for irrigation and agriculture in the regions it traverses, supporting millions of livelihoods.
⛰️ It originates from the Angsi Glacier in Tibet and is known as the Yarlung Tsangpo River in that region.
🌏 The Brahmaputra contributes significantly to the sediment load in the Bay of Bengal.
🦩 The river delta is one of the most fertile areas in the world, supporting rich biodiversity.
🚢 The Brahmaputra serves as an important waterway for transport and trade within the regions it flows through.
Brahmaputra River Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required