Kepler-69c Facts For Kids
Kepler-69c is a super-Earth exoplanet located in the habitable zone of its star, Kepler-69, and is known for its potential to support liquid water and possibly life.

Set reading age
View for Kids
Easy to read and understand
View for Students
Clear, detailed explanations
View for Scholars
Deep dives and big ideas
Introduction
Kepler-69c is a fascinating exoplanet, meaning it’s a planet that orbits a star outside our solar system! 🌌It was discovered in a galaxy far, far away, specifically in the constellation Lyra. This star system is about 2,700 light-years away from Earth. Imagine how far that is! To let you know how much that is, one light-year equals about 5.88 trillion miles! Kepler-69c is about 70% bigger than Earth, making it a "super-Earth!" Isn’t that amazing? 🌍✨
Gallery of Kepler-69c Facts For Kids
The Star Kepler-69
Kepler-69 is the star that Kepler-69c orbits. It is a type of star called a G-type star, just like our Sun! ☀️ Kepler-69 is located about 2,700 light-years away, and it is slightly cooler and smaller than the Sun. Interestingly, Kepler-69 is older than our Sun by about 3 billion years! 🌌This means that it has been shining in the universe for a really long time! Stars are crucial in helping us understand how planets like Kepler-69c can form and develop.
Exploration Missions
Currently, we haven’t sent any missions to visit Kepler-69c. 🤖However, scientists are studying it using telescopes! The Kepler Space Telescope helped find this planet, but it is now retired. 🚀Future missions may happen with more powerful telescopes, like the James Webb Space Telescope, which is working to look deeper into space and learn more about Kepler-69c and other exciting worlds beyond our solar system. Stay tuned for their discoveries! 🌠
Comparison With Earth
When we compare Kepler-69c with Earth, we see some interesting differences! 🌟Kepler-69c is about 1.7 times larger than Earth, which means it could have a stronger gravity, making people jump less! 🏃♂️ It also orbits its star every 242 days, while Earth takes 365 days for one complete orbit. So it experiences a shorter year! Kepler-69c might also have temperatures and climates that differ from Earth, but scientists are still studying those details to understand them better! 🌦️
Scientific Importance
Kepler-69c is important for scientists because it helps us learn about other planets and the possibilities of life beyond Earth. 🌌By studying planets in different star systems, scientists can understand how planets form, evolve, and maybe even host life! 🌱Kepler-69c’s position in the habitable zone makes it a key focus for searching for water, which is essential for life. Every discovery helps us piece together the grand puzzle of our universe! 🧩🌟
Habitability Potential
Kepler-69c is in the "habitable zone," which is like a special area around a star. 🌞This zone is where conditions might be just right for liquid water to exist, a major ingredient for life! While we don’t know for sure if Kepler-69c has water or not, the idea gives scientists hope! 🧪If liquid water exists, it could mean that other forms of life might survive there. Just like Earth, having water could create a perfect environment for plants or even aliens! 🌱👽
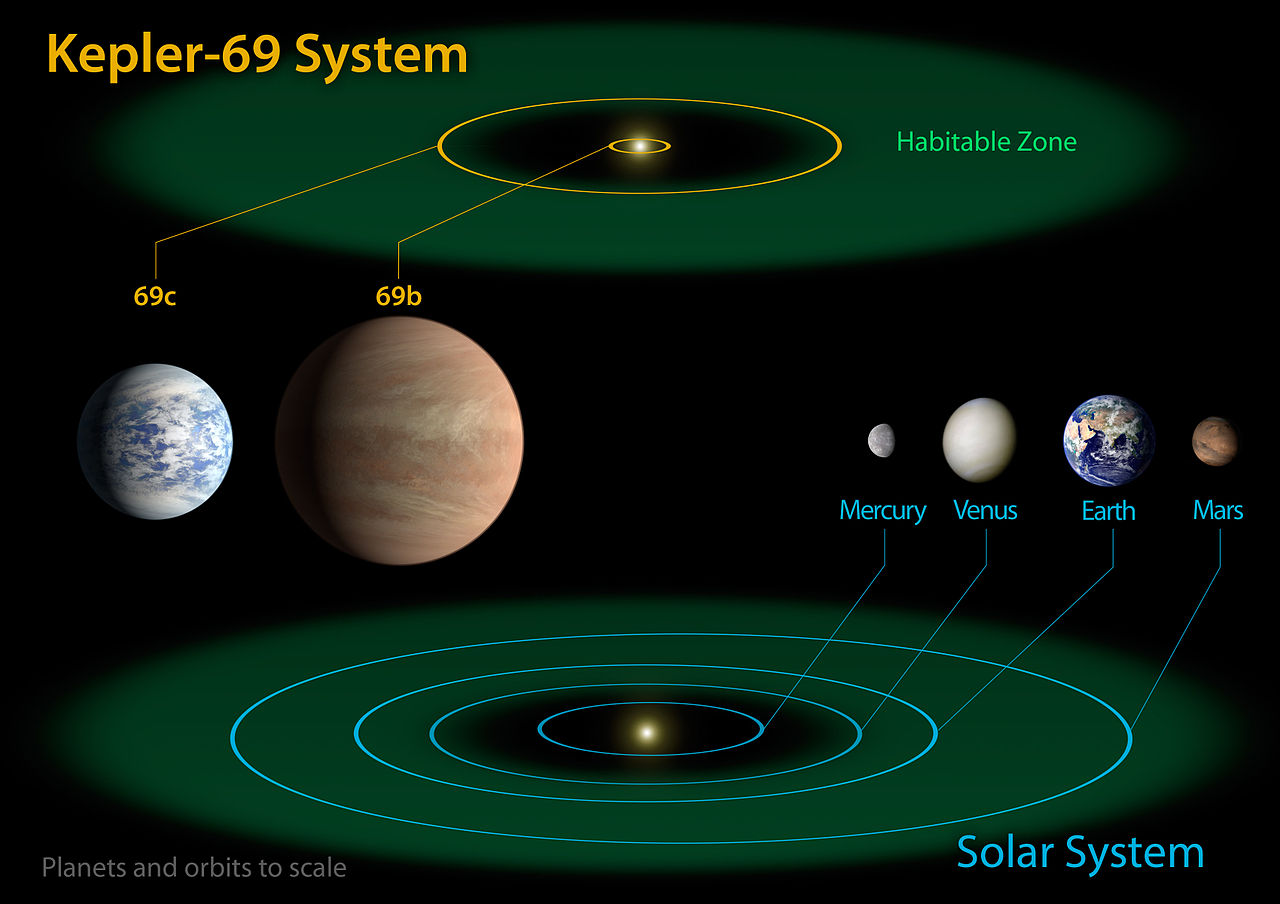
Discovery Of Kepler-69c
Kepler-69c was discovered by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope on July 23, 2013. 🔭The Kepler mission helped scientists find many planets by looking for little dips in starlight. 🌟When a planet passes in front of its star, it blocks some light, which Kepler can detect! The planet is part of the Kepler-69 system, which has two known planets altogether. Kepler-69c captured the interest of scientists because it orbits in the "habitable zone," where conditions might be right for water to exist! 💧
Future Research Directions
The future looks bright for researching Kepler-69c! 🌅Scientists hope to use advanced telescopes to learn more about its atmosphere and surface. They want to see if it really does have water or other signs of life! They also want to study more exoplanets like Kepler-69c around different stars. 🔭Exploring these new worlds will help us answer big questions about our universe, and who knows what amazing discoveries await us! 🪐So, keep looking up at the sky because we’re only beginning to explore! 🌌
Characteristics Of Kepler-69c
Kepler-69c is quite special! It’s about 1.7 times the size of Earth and is classified as a super-Earth due to its larger size. 🌏It takes around 242 days to orbit its star, Kepler-69, which is less than our Earth’s year! The planet surfaces could be rocky, or they could have oceans like Earth, but we’re not entirely sure yet! 🌊It’s exciting to think about what might be out there. The temperature on Kepler-69c might allow for liquid water – that’s why scientists are so interested!
Kepler-69c Facts For Kids Quiz


Make things. Learn new skills. Share safely.
DIY is a creative community where kids draw, build, explore ideas, and share.
No credit card required